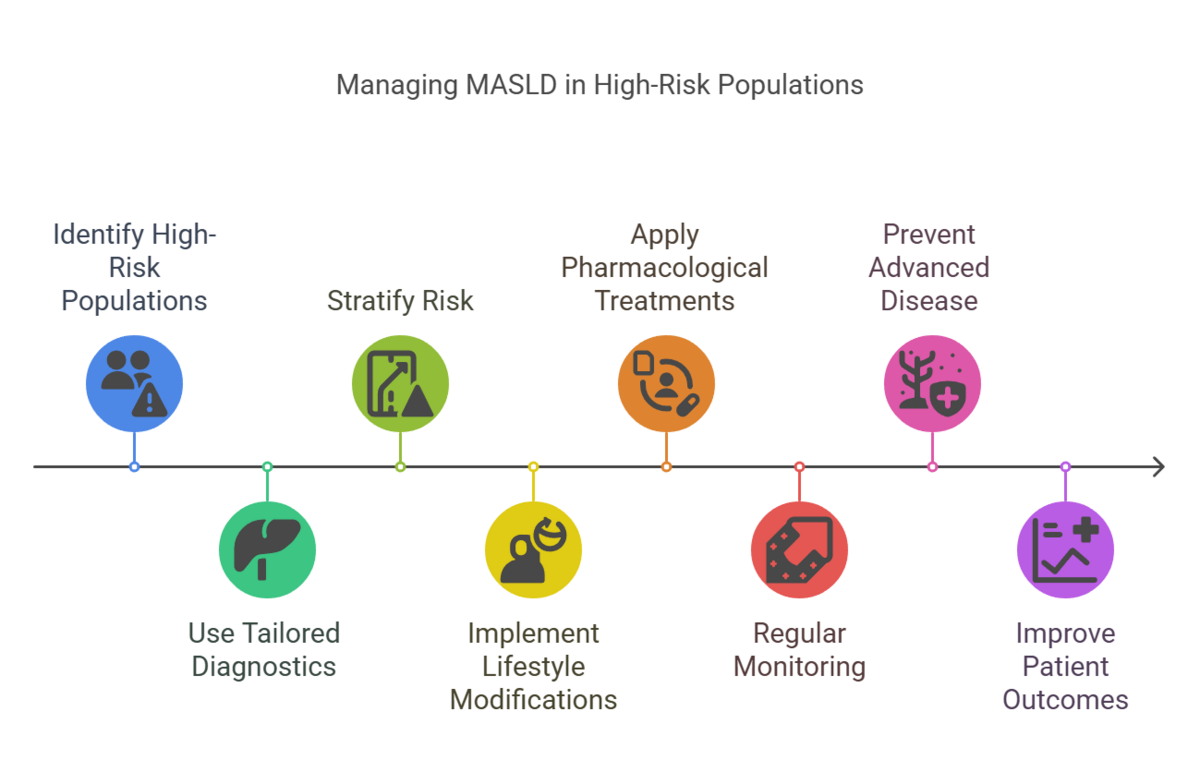
Metabolic Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) affects millions worldwide, but certain populations face significantly higher risks due to underlying metabolic conditions and lifestyle factors. Early identification and tailored interventions for these high-risk groups are critical in mitigating disease progression and improving outcomes.
In this post, we focus on identifying these populations and the role of personalized diagnostics and care strategies.
Who Is at Risk?
MASLD is closely linked to metabolic dysfunction, making individuals with certain conditions particularly vulnerable to the disease. Recognizing these high-risk groups allows healthcare providers to focus resources and interventions where they are needed most.
1. Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes
Research indicates that up to 70% of individuals with Type 2 diabetes also have MASLD, often progressing silently toward fibrosis or cirrhosis. The interplay between insulin resistance and liver fat accumulation accelerates liver damage in this group.
2. Patients with Obesity
Obesity is one of the strongest predictors of MASLD, affecting up to 90% of this population. Excess visceral fat contributes to liver fat deposition and inflammation, increasing the likelihood of progression to more severe disease stages.
3. Additional High-Risk Groups
· Individuals with Dyslipidemia: Elevated triglycerides and low HDL cholesterol are common in MASLD patients.
· Patients with Hypertension: Often part of metabolic syndrome, hypertension contributes to the overall disease burden.
· Family History of Liver Disease: Genetic predisposition can heighten MASLD risk.
Identifying these populations during routine care, such as diabetes or obesity management, provides an opportunity to diagnose MASLD early, even before symptoms appear.
The Importance of Tailored Diagnostics
For high-risk populations, non-invasive diagnostic tools are invaluable in stratifying patients by their risk of progression and guiding care decisions.
M30 Apoptosense® ELISA
Biomarkers like M30 Apoptosense® ELISA measure hepatocyte apoptosis, offering a non-invasive way to detect early liver injury. In high-risk groups, M30 can be used to:
· Identify patients likely to progress to advanced disease stages.
· Monitor the effectiveness of lifestyle or medical interventions.
· Provide a measurable outcome to guide therapeutic decisions.
The Benefits of Tailored Diagnostics
· Risk Stratification: Directs resources toward patients at highest risk, avoiding unnecessary testing for low-risk individuals.
· Proactive Monitoring: Allows clinicians to track changes over time and intervene when needed.
· Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces healthcare expenditures by preventing advanced-stage complications.
By focusing on non-invasive, scalable tools, healthcare providers can effectively manage MASLD in high-risk populations without relying on resource-intensive methods like biopsies.
Targeted Interventions for High-Risk Groups
Once high-risk patients are identified, personalized interventions can significantly improve outcomes and prevent progression to severe disease stages.
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes remain the cornerstone of MASLD management. Evidence shows that:
· Losing 7–10% of body weight can reduce liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis.
· Adopting a Mediterranean diet can improve liver health by emphasizing whole foods, healthy fats, and reduced sugar intake.
· Structured exercise programs improve metabolic function and reduce liver fat.
2. Pharmacological Treatments
Emerging therapies targeting specific mechanisms of MASLD, such as liver fat accumulation or fibrosis, are becoming available. These treatments complement lifestyle changes in patients who require additional intervention.
3. Regular Monitoring
Tools like M30 Apoptosense® ELISA enable healthcare providers to track the impact of interventions and make timely adjustments. Regular follow-ups also reassure patients of their progress, encouraging long-term adherence.
Preventing the Burden of Advanced Liver Disease
High-risk populations are at an increased likelihood of progressing to cirrhosis, liver failure, or hepatocellular carcinoma. The long-term economic and clinical burden of these outcomes is substantial. By focusing on early diagnosis and targeted interventions:
· The progression to severe disease can be significantly reduced.
· Patient quality of life improves.
· Healthcare systems can avoid the high costs associated with advanced-stage treatments.
Conclusion
Targeting high-risk populations with tailored diagnostics and interventions is a critical step in addressing the global burden of MASLD. Non-invasive tools like M30 Apoptosense® ELISA, combined with lifestyle changes and emerging therapies, provide healthcare providers with the resources needed to deliver proactive, patient-centered care.
As MASLD continues to rise worldwide, adopting this targeted approach will play a pivotal role in improving outcomes and reducing the disease’s impact on patients and healthcare systems. Read more here!