For U.S. users: The VLVbio K18 assays have not been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
NAFLD & NASH
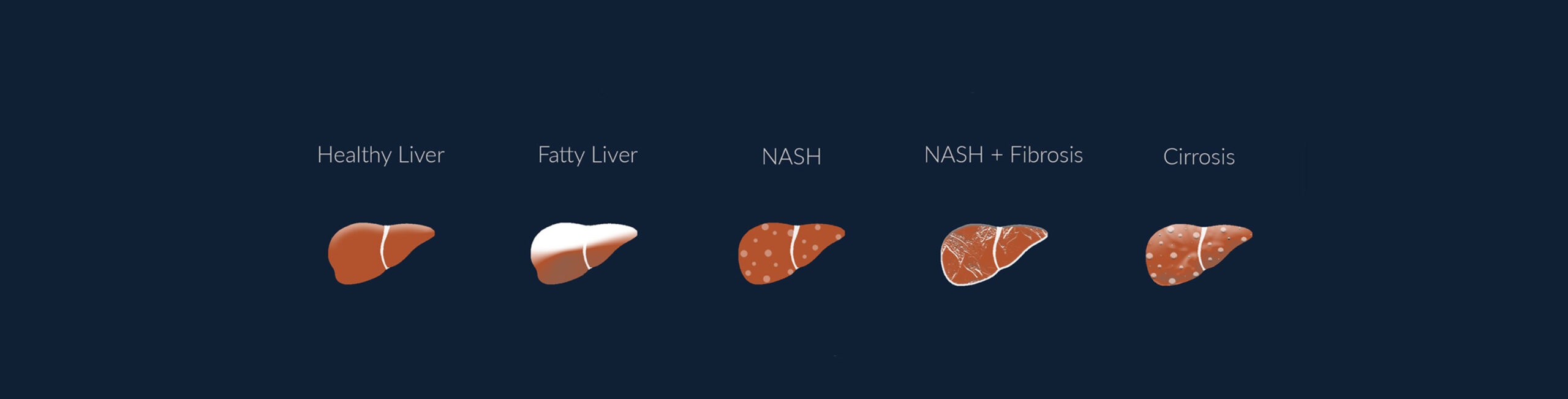
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition where fat accumulates in the liver without the excess consumption of alcohol, has become the most common cause of liver disease in the Western world, and is quickly rising to become the primary cause of liver transplants. Due to the rise in obesity and diabetes, NAFLD is estimated to affect 30 % of the global population, with a high prevalence on all continents.
This increase is most likely related to the so-called Western lifestyle; fast food, lifestyle changes, and reduced physical activity. NAFLD starts out as steatosis which is an accumulation of fat in the liver and may further progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a more serious form of NAFLD, where the liver has become inflamed. NASH is a potentially fatal condition that affects around 5% of the global adult population and can further develop into creation of fibrotic tissue in the liver, with possible cirrhosis as a result.
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE
Keratin-18 in NAFLD
Keratin 18 (K18) is an intermediate filament protein forming part of the cytoskeletal structure expressed in epithelial cells. Hepatocytes, a form of epithelial cell, are the main tissue cells found in the liver. When simple steatosis in NAFLD is accompanied by inflammation of hepatocytes, the disease is described as NASH.
This prominent characteristic of the disease is mainly caused by hepatocyte cell death due to apoptosis. Early on in the apoptosis of hepatocytes, caspases are activated which cleave the K18 protein, and the resulting fragments are subsequently released into the blood. These caspase cleaved K18 (ccK18) fragments can be efficiently quantified by the unique M30 Apoptosense® ELISA. Standard biomarkers of liver injury can be valuable tools to indicate a problem with the liver, but are non-specific and may perform poorly in the early detecting of NAFLD and NASH.
Therefore, it is essential to complement the use of standard biomarkers in order to increase the accuracy for detecting and stratifying NAFLD and NASH patients at an early stage, before advancements into end stage liver disease.
During early stages of NAFLD, the patient is often asymptomatic, and lifestyle intervention may help reverse the disease. However, it is much more difficult to reverse late stage liver disease where fibrosis has developed in large parts of the liver. Hence, a non-invasive early stage detection of NAFLD is important.
M30® levels in patients with NAFLD:
The M30 Apoptosense® ELISA allows for the significant discrimination between NASH and NAFLD or healthy individuals, while also distinguishing between NAFL and healthy controls.
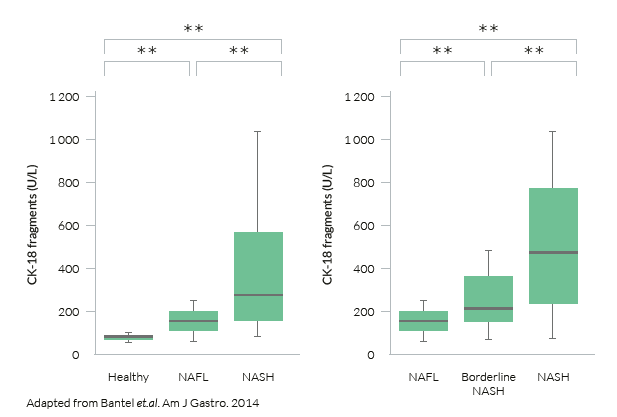
Hence, the M30 Apoptosense® can allow for early identification of patients that should be further sent to specialist secondary care for further assessment of damage to the liver.
How to implement the M30 Apoptosense® into clinical practice
In combination with FIB-4
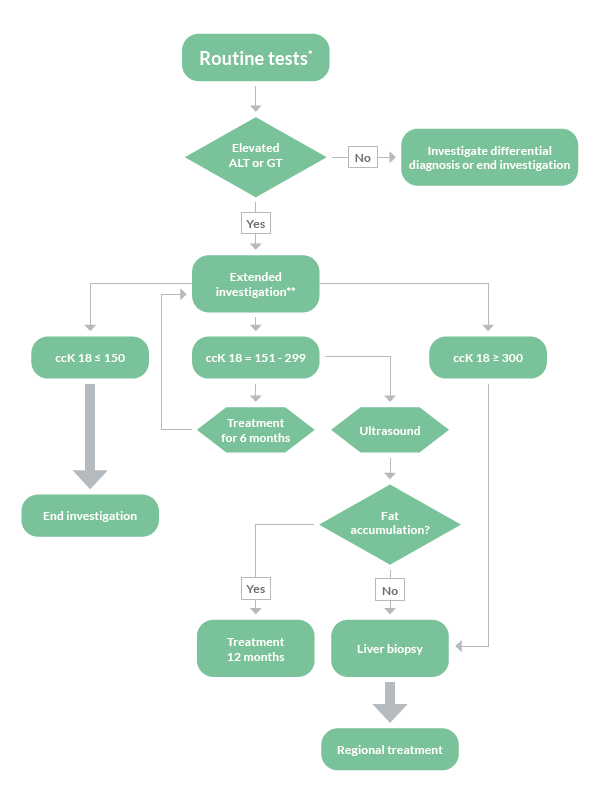
There is a great need to non-invasively assess patients at risk of developing NASH and fibrosis already at primary care. By using Non-Invasive Tests to evaluate risk group patients already at primary care, only patients at highest risk of disease progression and liver related complications will proceed to a specialist in secondary care for further investigation.
FIB-4 has shown to be a valuable tool to exclude advanced fibrosis, and is widely recommended in clinical guidelines to be used. The combination of the M30 Apoptosense® ELISA with FIB-4 could enable a more reliable identification of patients with increased risk of progressed NAFLD and might be helpful for deciding which patient should be referred to a specialist and considered for liver biopsy.
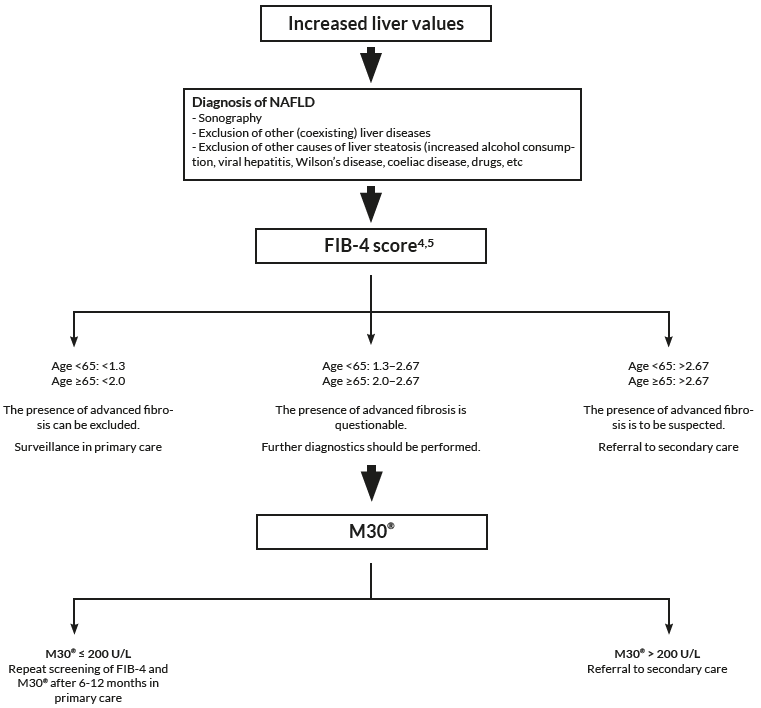
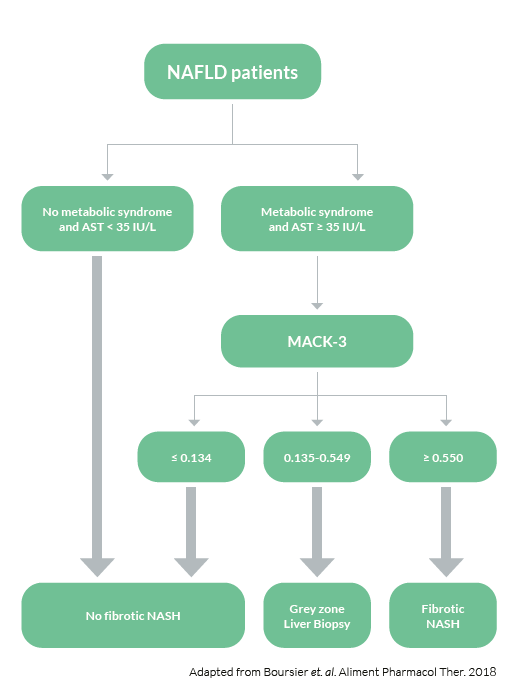
To asses fibrotic NASH
Detecting fibrotic NASH patients has become important in order to identify those patients most likely to benefit from treatment intervention. The common criteria used for identifying fibrotic NASH are NAS≥4 and fibrosis tage F≥2. M30 Apoptosense® ELISA is a sensitive and specific biomarker for hepatocyte apoptosis and can greatly increase the accuracy of biomarker panels for fibrotic NASH.
To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of blood fibrosis tests, Boursier et al. compared NFS, BARD score and FIB-4 with biomarkers of metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, liver inflammation and M30® for the diagnosis of fibrotic NASH in a study on 846 subjects with biopsy proven NAFLD. Data for these biomarkers were then used to develop a new biomarker panel aimed at improving the
diagnostic accuracy of NAFLD. The new blood test, MACK-3, accurately diagnoses fibrotic NASH. This new test will facilitate patient screening and inclusion in NAFLD therapeutic trials and will enable the identification of patients who will benefit from the treatments once approved.
The MACK-3 score can be used in the clinic in the following way:
For pediatric NAFLD
As children can develop a harmful stage of NAFLD faster than adults, it is of utmost importance to identify children at risk of liver injury. The M30 Apoptosense® ELISA has long been studied as an indicator of liver injury (steatosis and NASH) in pediatric patients and is today being used in clinical settings to screen patients with childhood obesity, and can be implemented into pediatric NAFLD care in the following way: