Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis
About NASH
NASH is a progressive and serious form of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), and has during the last couple of decades become one of the most common causes of liver disease globally and a public health problem. The number of affected patients is growing rapidly and the disease affects a considerable share of today’s global population.The incidence of NAFLD worldwide is reported to be around 20–35%, and of these around 10–30% have NASH. In absolute numbers this would mean that around 375 million suffer from NASH. Within the obese and diabetic population, the number of NAFLD and NASH patients is much higher, sometimes reported to be as high as 75–95% and 40% respectively.

NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS
NASH
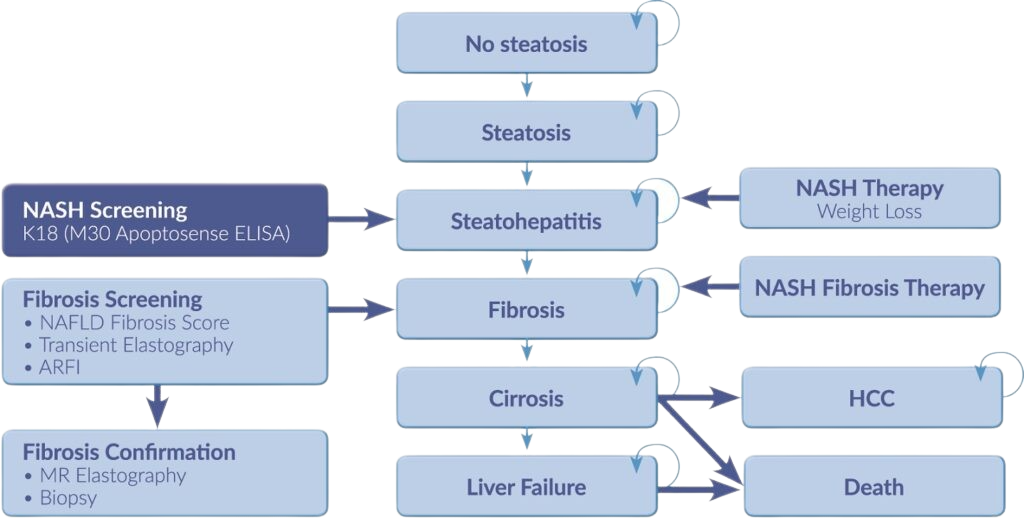
It is projected that NAFLD and NASH will become the major cause of liver related morbidity and mortality during the next decade. NASH is characterized as simple steatosis accompanied by inflammation, cell injury and ballooning, with or without fibrosis. It can progress to cirrhosis, liver failure and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and is associated with dramatically increased liver-related and cardiovascular mortality.
The inflammation of hepatocytes described in NASH is a prominent characteristic of the disease, mainly caused by hepatocyte cell death due to apoptosis. Early on in the apoptosis of hepatocytes, caspases (a form of proteases) are activated and cleave the protein keratin 18 (K18), and the resulting fragments are subsequently released into the blood. These K18 fragments can be efficiently quantified by the unique M30 Apoptosense® ELISA.
The model illustrates the natural history of NAFLD, and screening strategies and therapies for the treatment of the disease.
M30 Apoptosense® ELISA – A reliable non-invasive tool for the detection and screening of NASH
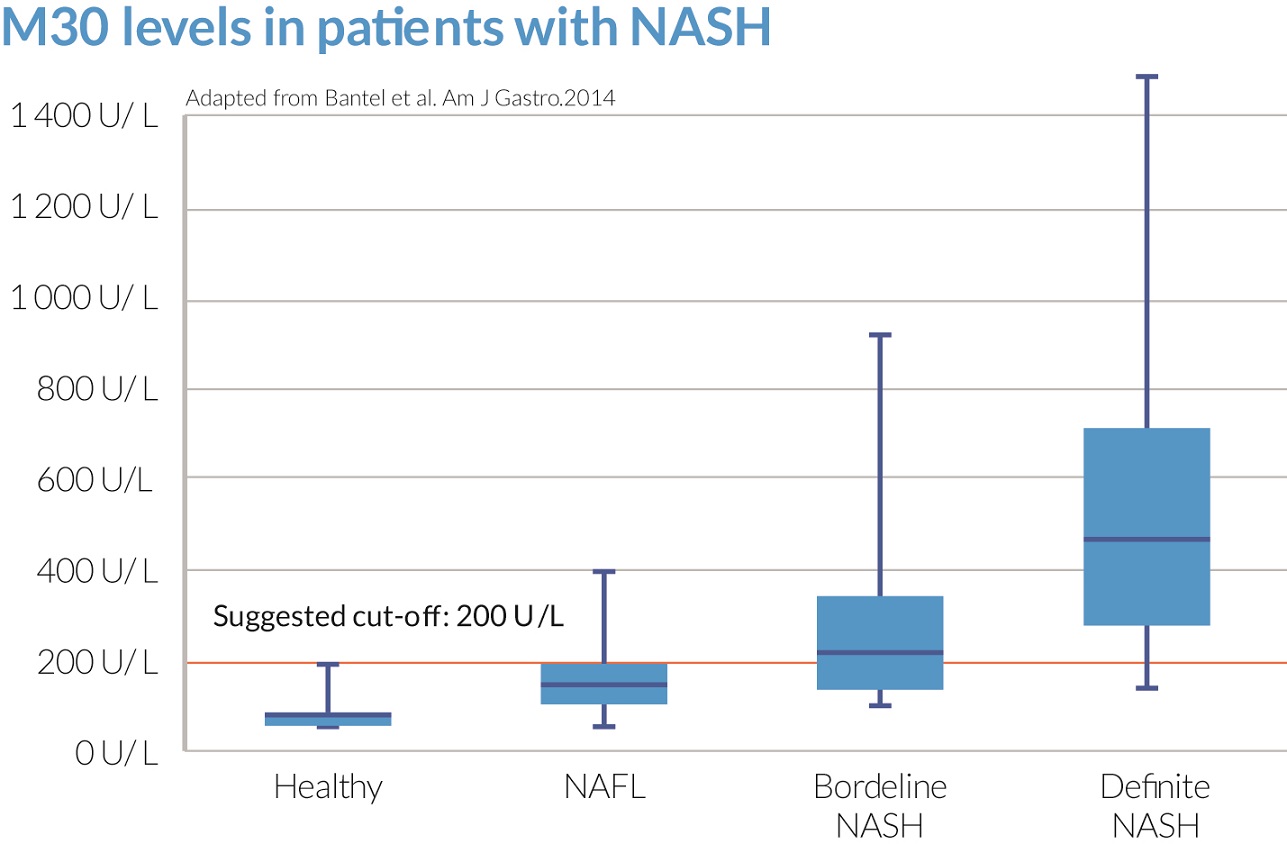
The M30 Apoptosense® ELISA measures the concentration of K18 fragments and is a specific and reliable tool for the detection and screening of NASH. Two recent meta-analyses demonstrated that levels of K18 fragments predict the presence of NASH with a pooled AUROC of 0.82, 78 % sensitivity and 86 % specificity and AUROC of 0.8445, 83 % sensitivity and 71 % specificity, respectively.
The figure shows that the M30 Apoptosense® ELISA allows the significant discrimination between NASHand NAFL, as well as between NASH and healthy. Furthermore, the M30 Apoptosense® ELISA can distinguish between NAFL and borderline NASH.
Read more about the VLVbio K18 assays in NASH

PRODUCT
M30 Apoptosense® ELISA
The M30 Apoptosense® ELISA assay is based on the unique M30® antibody that recognizes a neo-epitope of keratin 18 (K18), formed after caspase cleavage during apoptosis. The M30 Apoptosense® ELISA is CE marked as a medical device for in vitro diagnostic use.
PRODUCT
M65® ELISA
The assay, based on the M5 and the M6 antibodies, measures total cell death due to apoptosis or necrosis and is intended for human serum or plasma. The assay is CE marked as a medical device for in vitro diagnostic use.
